Dry-running plates
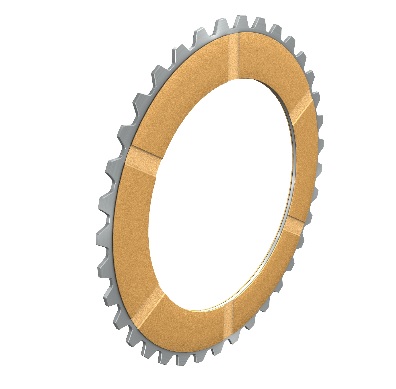
Generally dry-running clutches and brakes use a pair of plates consisting of "organic" friction lining on one plate and a counterplate of steel or special cast iron. Although this friction combination is subject to wear, it has become a standard due to its hard wearing capabilities. Sintered, metallic friction linings are also used for particular applications. The friction linings described here are riveted or bonded to the plates in the form of rings or segments or are applied by a sintering process.
Wet-running plates

When considering "wet-running" plates, it is necessary to consider the lubricating and cooling oil, since this plays a decisive roll in the frictional process. In wet-running clutches and brakes the "classical" friction combination of steel/steel is today being replaced more and more by steel/sintered coating. The standard qualities of sintered coating are able to cover a wide range of conditions which are placed on high performance friction linings. In addition, the sinter is capable of being varied in terms of composition porosity and compatibility with oil enabling it to fulfill a wide range of special tasks. Of special interest within the range of wet- running plates is the friction combination steel/paper lining. This is being used to an ever greater extent in transmission systems in general mechanical engineering and in the motor vehicle industry. This is due to its extraordinary frictional behaviour and its almost total freedom from wear.
Wet-running sinter-lining plates
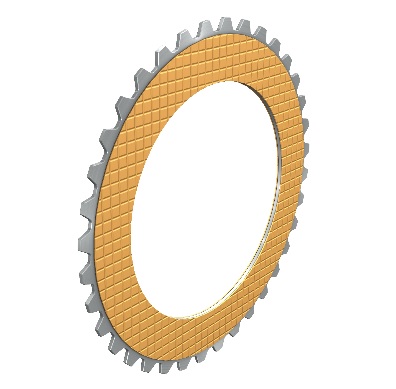
High thermal load
Broad power spectrum due to high allowable surface pressures
None to little wear
Hardened steel counterplate, typical with sinus corrugation
Good oil distribution via wafer or sunburst keyway
Applications:
- Press technology
- Marine main drives
- Brakes with high thermal loads
- Gearbox with high thermal loads
Dry-running sinter-lining plates
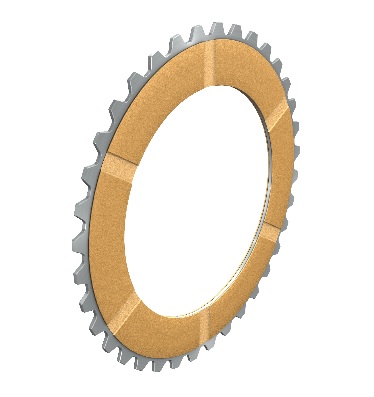
Medium thermal loads
High surface pressures
Low wear rates
Hardened counterplate, flat steel plates
Radial keyways for removal of abraded material
Applications:
- Brakes
- Clutches
- Slip clutches
Wet-running paper plates
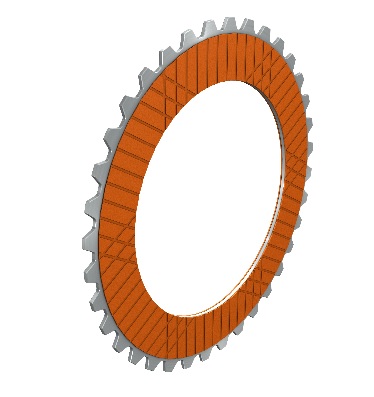
Moderate to high thermal load
Low surface pressures
Low to moderate wear properties
Constant friction value via speed, good controllability
Steel counterplate with sinus (hardened and unhardened)
Good comfort behavior
Oil distribution via group parallel or wafer keyway
Applications:
- Winding
- Unwinding jig with continuous slip operations
- Controlled overload clutches
Dry-running organic-lining plates

Moderate thermal load capacity
High friction values
Moderate to high wear
Steel or cast iron counter friction surfaces
Applications:
- Brakes
- E clutches
- Pneumatic combined c/b
- Overload clutch
Steel plates
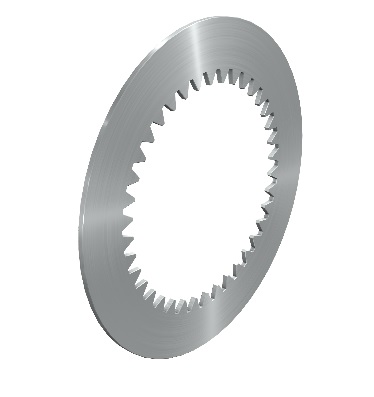
Version with sinus or flat
In hardened or unhardened version
Coating possible (e.g. molybdenum)
Surface areas are furnished with specific structures
Plates with splines
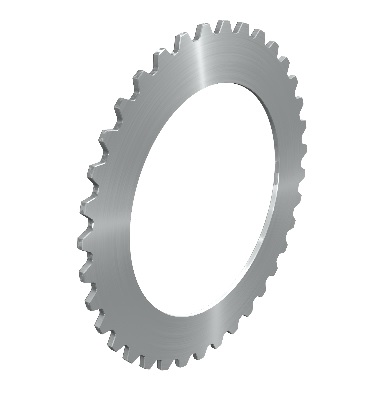
High torque transmissibility
Self-centering
Low plate strength possible
Use in limited installation spaces
Plates with lugs
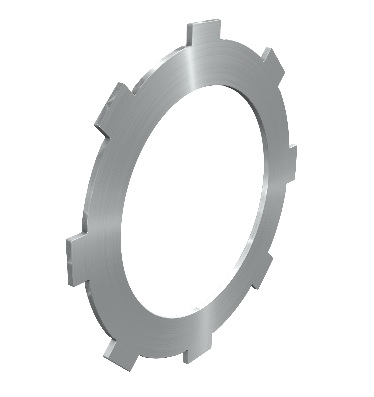
Counter profiles can be easily produced
Applications with small to medium torques
Applications:
- Small clutches and brakes
- E clutches/brakes
Dry-running organic-lining plates

Counter profiles can be easily produced
Applications with small to medium torques
Applications:
- Small clutches and brakes
- E clutches/brakes
Plates with rounded lugs

Counter profiles can be easily produced
Centering effect possible
Applications:
- Small clutches and brakes
- E clutches/brakes